As we enter the new year, it is time to reflect on the past achievements and challenges of the digital health sector, and to look ahead at the emerging opportunities and innovations that will shape the future of healthcare. Here are some of the key trends that will dominate the digital health landscape in 2024.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and ML are transforming the healthcare industry in unprecedented ways. From improving diagnosis and treatment to enhancing patient engagement and satisfaction, these technologies are enabling smarter and more personalized care. Some examples of AI and ML applications in digital health are:
- Virtual assistants that provide health information, reminders, and support to patients and caregivers.
- Computer vision and natural language processing that analyze medical images and reports to detect anomalies, diseases, and risks.
- Data analytics and predictive modeling that identify patterns, trends, and insights from large and complex health data sets.
- Clinical decision support systems that assist doctors and nurses with diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up recommendations.
AI and ML are not only enhancing the quality and efficiency of healthcare, but also creating new opportunities for innovation and collaboration.
Remote Monitoring & Telehealth.
One of the most prominent trends is the rise of remote monitoring and telehealth solutions, which enable patients to receive care and support from anywhere, anytime. Remote monitoring and telehealth are not new concepts, but they have gained momentum and popularity during the COVID-19 pandemic, as social distancing and lockdown measures have limited access to traditional healthcare settings.
Remote monitoring and telehealth offer many benefits for both patients and providers, such as:
Improved access and convenience: Patients can access care and support from the comfort of their homes, workplaces, or other locations, without having to travel or wait for appointments. This is especially beneficial for rural and underserved populations, as well as for people with chronic conditions, disabilities, or mobility issues.
Reduced costs and inefficiencies: Remote monitoring and telehealth can reduce the need for hospitalizations, emergency visits, and readmissions, as well as lower the overhead costs associated with physical facilities and staff.
Enhanced patient engagement and satisfaction: Remote monitoring and telehealth can empower patients to take more control over their own health and wellness, by providing them with real-time feedback, personalized guidance, and tailored interventions.
Some of the technical enablers for that to happen:
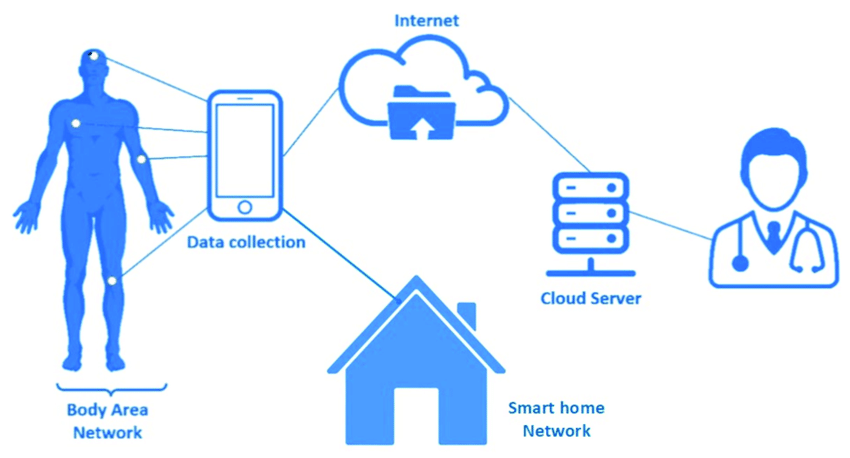
- Wearable devices and sensors: These are devices that can be worn or attached to the body, such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, patches, or implants, that can measure various physiological parameters, such as heart rate, blood pressure, glucose levels, oxygen saturation, temperature, etc. These devices can transmit the data to a smartphone app or a cloud-based platform, where it can be analyzed and shared with the patient’s provider or caregiver.
- Mobile apps and platforms: These are applications or software that can be accessed through a smartphone, tablet, or computer, that can provide various functions, such as symptom tracking, medication reminders, health education, coaching, counseling, etc. These apps can also facilitate communication and interaction between patients and providers via text messages, voice calls, video calls, chatbots, etc.
- Smart home devices and systems: These are devices or systems that can be installed or integrated into the home environment, such as smart speakers, cameras, monitors, alarms, etc., that can provide various services, such as remote surveillance, fall detection, emergency response, medication dispensing, etc. These devices can also connect with other smart home devices or systems via the Internet of Things (IoT), such as smart thermostats, lighting systems, security systems, etc., to create a more comfortable and safe living space for the patient.
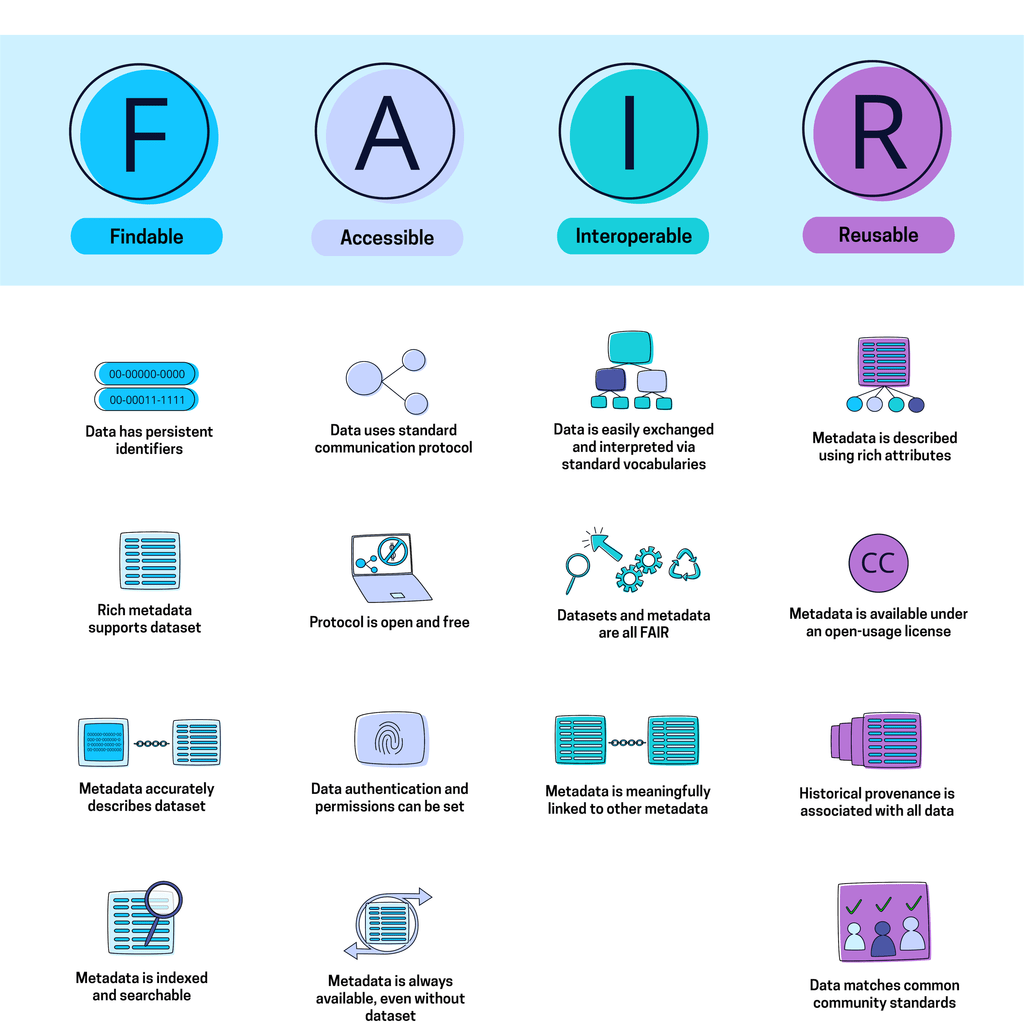
FAIR and Secure Data
As digital health solutions become more prevalent and sophisticated, the need for reliable and secure data management also increases. One of the emerging trends in this field is the adoption of FAIR principles, which stand for Findable, Accessible, Interoperable and Reusable. FAIR data aims to improve the quality, transparency and usability of health data, while also ensuring its protection and privacy. FAIR data can help health organizations to leverage data analytics, artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance their services, outcomes and efficiency. For example, FAIR data can enable researchers to share and reuse data from different sources and domains, such as clinical trials, electronic health records, genomics, wearables and social media.
Some of the use cases that comes to my mind:
- Developing a FAIR data platform for epidemiology research, which allows researchers to access and integrate data from various sources, such as epidemiological, clinical, genomic and environmental data, to understand the transmission, diagnosis, treatment and prevention of the disease.
- Applying FAIR data principles to cancer research, which enables researchers to access and analyze data from different types of cancer, such as breast, lung, prostate and colorectal cancer, and to identify common patterns, biomarkers and potential therapies across different cancers.
- Implementing FAIR data standards for rare diseases, which helps researchers and clinicians to find and use data from patients with rare diseases, such as cystic fibrosis, muscular dystrophy and Huntington’s disease, and to improve the diagnosis, management and treatment of these conditions.
However, FAIR data also poses new challenges for cyber security. As health data becomes more widely available and shared, it also becomes more vulnerable to cyber-attacks, data breaches and misuse. Therefore, cyber security measures need to be strengthened and aligned with FAIR data standards, such as encryption, authentication, authorization and auditing. Cyber security is not only a technical issue, but also a cultural and ethical one, requiring awareness, education and collaboration among all stakeholders in the digital health ecosystem.
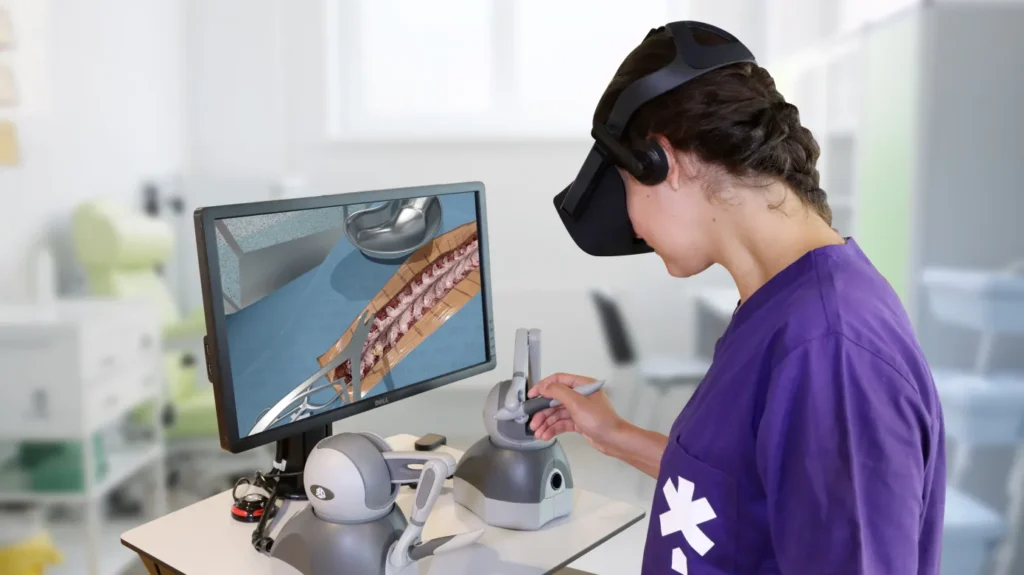
Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality
AR and VR are revolutionizing the healthcare sector in multiple ways. They can provide realistic and immersive training opportunities for medical students and professionals, especially in surgery. AR and VR can enable them to hone their skills and learn from their mistakes without risking any patient’s life. AR and VR can also enhance collaboration and communication among surgeons, as well as patient outcomes and satisfaction.
For the patients, AR and VR can help them cope with chronic pain, anxiety, or phobias by creating interactive and immersive environments that can alleviate their distress or help them overcome their fears in a safe way. AR and VR can offer effective and engaging simulations that can improve the quality and effectiveness of health interventions.

Predictive Care
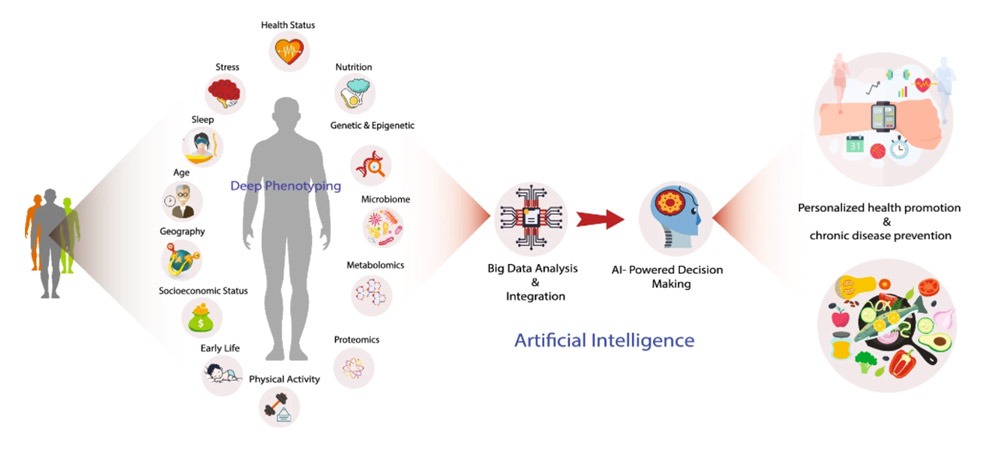
One of the most promising and innovative trends I anticipate in 2024 is the transition from reactive to predictive care. This means that instead of only seeking medical help when symptoms arise, people will use digital tools and data to monitor the risk of getting sick and receive tailored advice for prevention and wellness. By using predictive care, people will be able to enhance their quality of life, lower healthcare expenses, and prevent chronic diseases.
Some examples of predictive care are:
- Wearable devices that monitor vital signs, activity levels, and sleep patterns, and alert users and their doctors of any anomalies or risks.
- Smart home systems that detect changes in behavior, mood, or cognition, and provide personalized interventions or recommendations.
- Genomic testing that reveals genetic predispositions to certain diseases, and enables tailored prevention and treatment plans.
- Telehealth platforms that connect patients with health professionals, and provide real-time feedback and guidance.
Conclusion
These are just some of the trends that I think will shape the future of digital health in 2024.
Of course, there are many more factors that will influence the direction and pace of innovation in this field, such as regulation, policy, funding, ethics, and social acceptance.
I am excited to see what the new year will bring, and I hope you are too.
What are your thoughts on the digital health trends in 2024?
Please share your comments below.